Azure-Advanced-Networking
M01-Unit 8 Connect two Azure Virtual Networks using global virtual network peering
Exercise scenario
In this unit, you will configure connectivity between the CoreServicesVnet and the ManufacturingVnet by adding peerings to allow traffic flow.
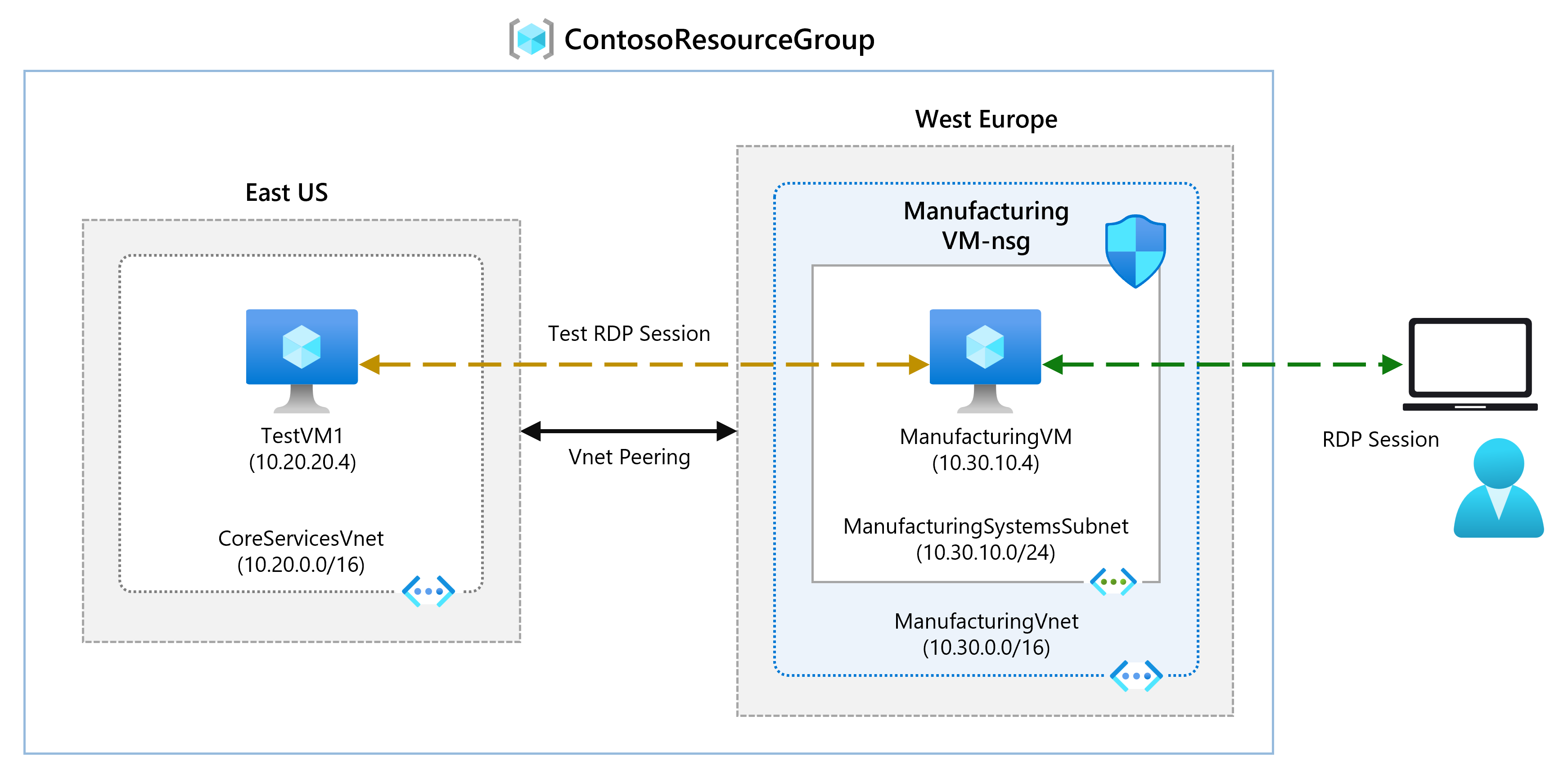
In this unit, you will:
- Task 1: Create a Virtual Machine to test the configuration
- Task 2: Connect to the Test VMs using RDP
- Task 3: Test the connection between the VMs
- Task 4: Create VNet peerings between CoreServicesVnet and ManufacturingVnet
- Task 5: Test the connection between the VMs
-
Task 6: Clean up resources
Note: An interactive lab simulation is available that allows you to click through this lab at your own pace. You may find slight differences between the interactive simulation and the hosted lab, but the core concepts and ideas being demonstrated are the same.
Estimated time: 20 minutes
Task 1: Create a Virtual Machine to test the configuration
In this section, you will create a test VM on the Manufacturing VNet to test if you can access resources inside another Azure virtual network from your ManufacturingVnet.
Create ManufacturingVM
-
On the Azure portal, open the PowerShell session within the Cloud Shell pane.
-
On the toolbar of the Cloud Shell pane, select the Manage files icon, in the drop-down menu, select Upload and upload the following files ManufacturingVMazuredeploy.json and ManufacturingVMazuredeploy.parameters.json into the Cloud Shell home directory from the source folder C:\Allfiles\Exercises\M01.
-
Deploy the following ARM templates to create the VMs needed for this exercise:
Note: You will be prompted to provide an Admin password. Use Pa55w.rd1234abc
$RGName = "ContosoResourceGroup" New-AzResourceGroupDeployment -ResourceGroupName $RGName -TemplateFile ManufacturingVMazuredeploy.json -TemplateParameterFile ManufacturingVMazuredeploy.parameters.json -
When the deployment is complete, go to the Azure portal home page, and then select Virtual Machines.
-
Verify that the virtual machine has been created.
Task 2: Connect to the Test VMs using RDP
-
On the Azure Portal home page, select Virtual Machines.
-
Select ManufacturingVM.
-
On ManufacturingVM, select Connect > Connect.
-
On ManufacturingVM | Connect, select Download RDP file.
-
Select keep if prompted.
-
Connect to ManufacturingVM using the RDP file, and the username TestUser and the password Pa55w.rd1234abc.
-
On the Azure Portal home page, select Virtual Machines.
-
Select TestVM1.
-
On TestVM1, select Connect > Connect.
-
On TestVM1 | Connect, select Download RDP file.
-
Select keep if prompted.
-
Connect to TestVM1 using the RDP file, and the username TestUser and the password Pa55w.rd1234abc.
-
On both VMs, in Networks, select Yes.
-
On TestVM1, open a PowerShell prompt, and run the following command: ipconfig
-
Note the IPv4 address.
Task 3: Test the connection between the VMs
-
On the ManufacturingVM, open a PowerShell prompt.
-
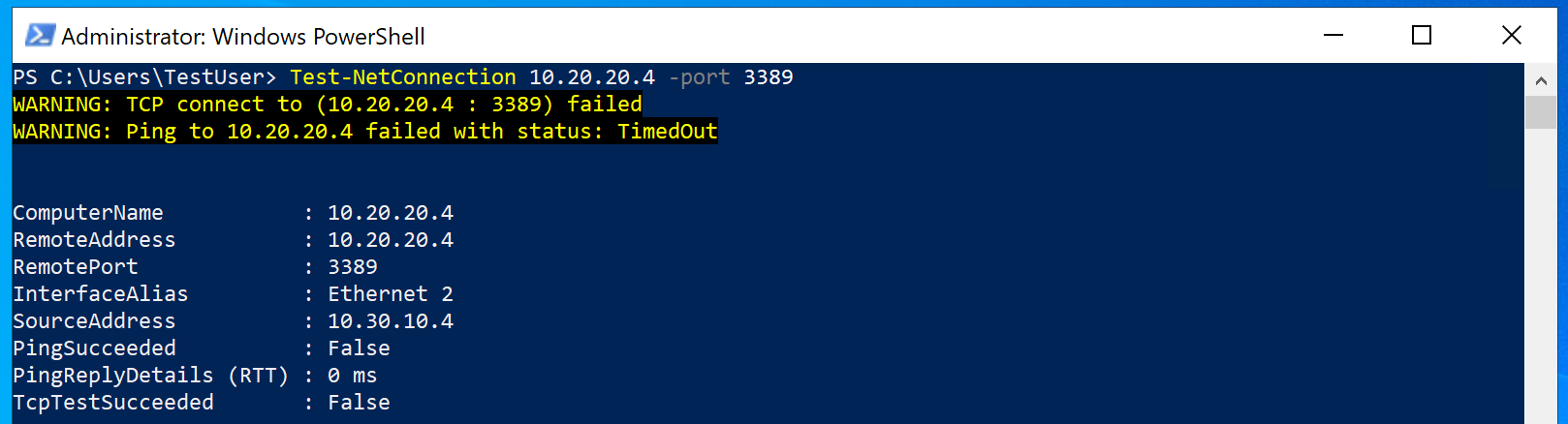
Use the following command to verify that there is no connection to TestVM1 on CoreServicesVnet. Be sure to use the IPv4 address for TestVM1.
Test-NetConnection 10.20.20.4 -port 3389 -
The test connection should fail, and you will see a result similar to the following:
Task 4: Create VNet peerings between CoreServicesVnet and ManufacturingVnet
-
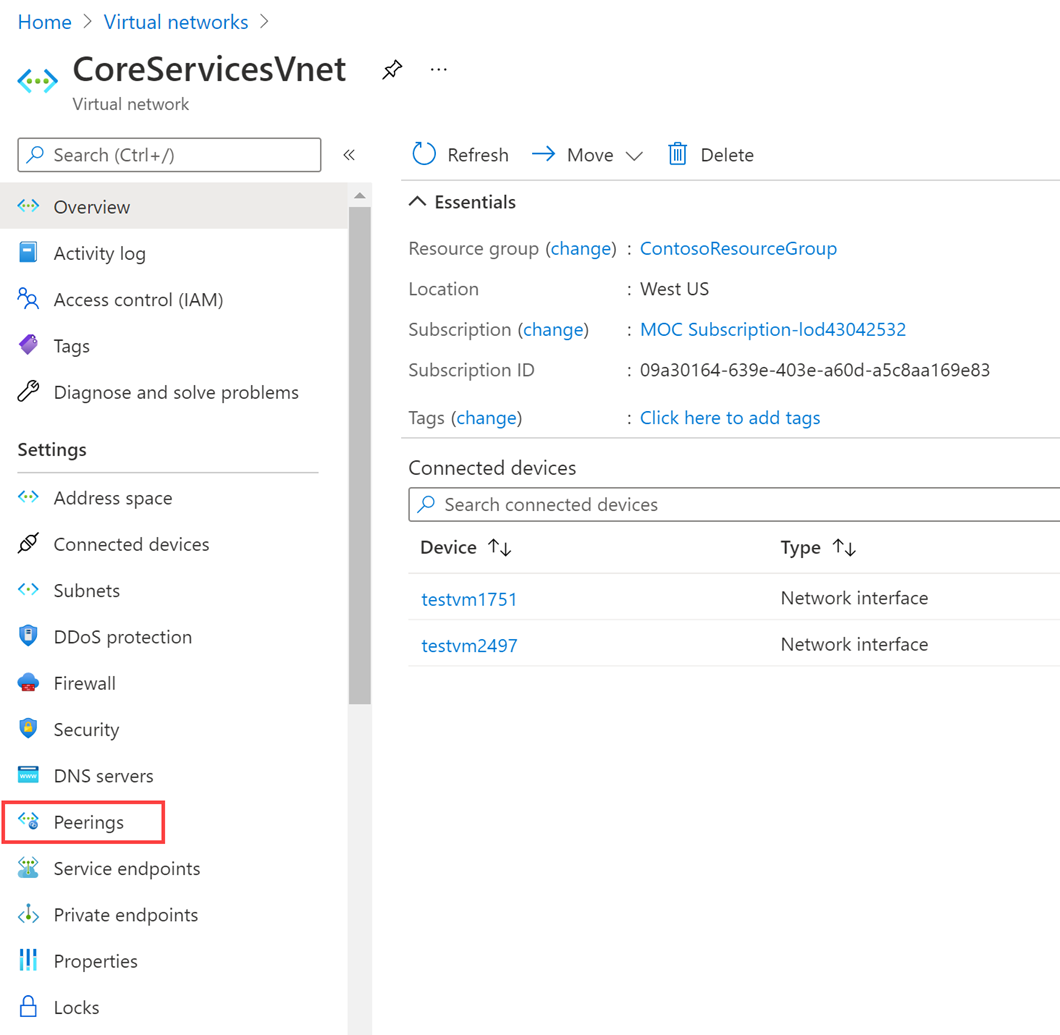
On the Azure home page, select Virtual Networks, and then select CoreServicesVnet.
-
In CoreServicesVnet, under Settings, select Peerings.
-
On CoreServicesVnet | Peerings, select + Add.
Use this information to create the peering. When finished, select Add.
Remote virtual network summary
| Option | Value |
|---|---|
| Peering link name | ManufacturingVnet-to-CoreServicesVnet |
| Virtual network | ManufacturingVnet |
Remote virtual network peering settings
| Option | Value |
|---|---|
| Allow ‘ManufacturingVnet’ to access ‘CoreServicesVnet’ | Enabled |
| Allow ‘ManufacturingVnet’ to receive forwarded traffic from ‘CoreServicesVnet’ | Enabled |
Local virtual network summary
| Option | Value |
|---|---|
| Peering link name | CoreServicesVnet-to-ManufacturingVnet |
Remote virtual network peering settings
| Option | Value |
|---|---|
| Allow ‘CoreServicesVnet’ to access ‘ManufacturingVnet’ | Enabled |
| Allow ‘CoreServicesVnet’ to receive forwarded traffic from ‘ManufacturingVnet’ | Enabled |
-
In CoreServicesVnet | Peerings, verify that the CoreServicesVnet-to-ManufacturingVnet peering is listed and Peering status says Connected..
Note: you may have to refresh the CoreServicesVnet | Peerings blade more than once.
-
Under Virtual networks, select ManufacturingVnet, and verify the ManufacturingVnet-to-CoreServicesVnet peering is listed and Peering status says Connected.
Note: you may have to refresh the ManufacturingVnet | Peerings blade more than once.
Task 5: Test the connection between the VMs
-
On the ManufacturingVM, open a PowerShell prompt.
-
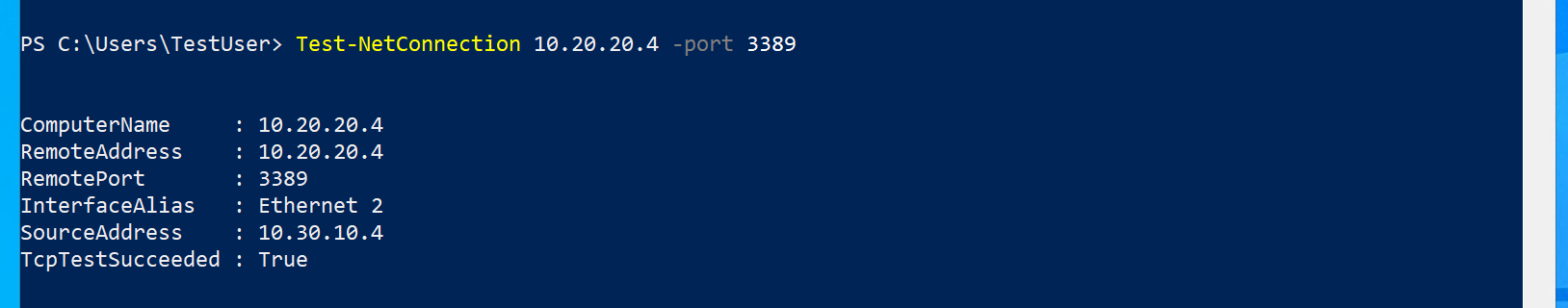
Use the following command to verify that there is now a connection to TestVM1 on CoreServicesVnet.
Test-NetConnection 10.20.20.4 -port 3389 -
The test connection should succeed, and you will see a result similar to the following:
Congratulations! You have successful configured connectivity between VNets by adding peerings.
Task 6: Clean up resources
Note: Remember to remove any newly created Azure resources that you no longer use. Removing unused resources ensures you will not see unexpected charges.
-
On the Azure portal, open the PowerShell session within the Cloud Shell pane. (Create Cloud Shell storage if needed, using default settings.)
-
Delete all resource groups you created throughout the labs of this module by running the following command:
Remove-AzResourceGroup -Name 'ContosoResourceGroup' -Force -AsJobNote: The command executes asynchronously (as determined by the -AsJob parameter), so while you will be able to run another PowerShell command immediately afterwards within the same PowerShell session, it will take a few minutes before the resource groups are actually removed.